Bootstrap Buttons Icon
Introduction
The button features coupled with the links wrapped inside them are possibly some of the most significant elements helping the users to have interaction with the web pages and move and take various actions from one webpage to some other. Specifically now in the mobile first environment when at least half of the pages are being observed from small-sized touch screen machines the large comfortable rectangle places on screen very easy to locate with your eyes and touch with your finger are even more necessary than ever. That's why the new Bootstrap 4 framework progressed delivering even more comfortable experience canceling the extra small button sizing and adding some more free space around the button's captions to make them more legible and easy to apply. A small touch providing a lot to the friendlier appearances of the brand new Bootstrap Button How are additionally just a bit more rounded corners which along with the more free space around helping to make the buttons so much more satisfying for the eye.
The semantic classes of Bootstrap Buttons Twitter
Here in this version that have the identical amount of great and easy to use semantic styles providing the feature to relay explanation to the buttons we use with simply adding a special class.
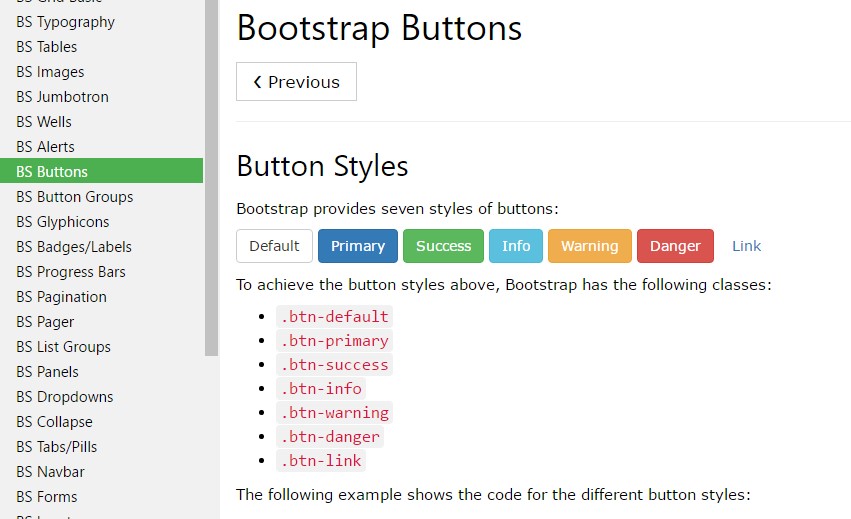
The semantic classes are the same in number just as in the last version still, with a number of upgrades-- the hardly used default Bootstrap Button Twitter generally having no meaning has been cancelled in order to get changed by more subtle and user-friendly secondary button styling so in a moment the semantic classes are:
Primary .btn-primary - painted in soft blue;
Info .btn-info - a little bit lighter and friendlier blue;
Success .btn-success the good old green;
Warning .btn-warning colored in orange;
Danger .btn-danger that comes to be red;
And Link .btn-link which comes to style the button as the default url component;
Just assure you first incorporate the main .btn class just before using them.

<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Primary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary">Secondary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-success">Success</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-info">Info</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-warning">Warning</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-danger">Danger</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-link">Link</button>Tags of the buttons
The .btn classes are constructed to be used with the <button> element. You can also use these classes on <a> or <input> elements (though some browsers may apply a just a little different rendering). When ever making use of button classes on <a> elements which are used to provide in-page functions (like collapsing content), instead linking to new web pages or zones within the current webpage, these web links should be granted a role="button" to effectively convey their function to assistive technologies such as display screen viewers.
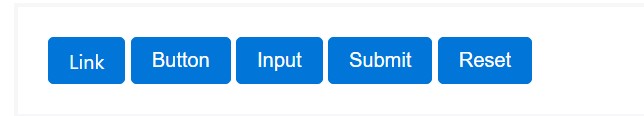
<a class="btn btn-primary" href="#" role="button">Link</a>
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">Button</button>
<input class="btn btn-primary" type="button" value="Input">
<input class="btn btn-primary" type="submit" value="Submit">
<input class="btn btn-primary" type="reset" value="Reset">These are however the one-half of the attainable appearances you can include in your buttons in Bootstrap 4 ever since the new version of the framework additionally provides us a brand-new slight and interesting solution to style our buttons holding the semantic we currently have-- the outline process.
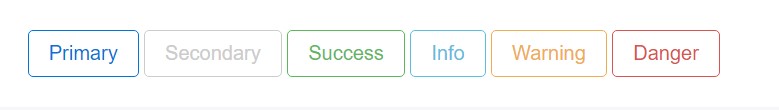
The outline process
The pure background without border gets substituted by an outline having some text message with the equivalent color. Refining the classes is definitely easy-- simply add in outline right before assigning the right semantics like:
Outlined Major button comes to be .btn-outline-primary
Outlined Secondary - .btn-outline-secondary and so on.
Significant fact to note here is there is no such thing as outlined web link button so the outlined buttons are really six, not seven .
Change the default modifier classes with the .btn-outline-* ones to clear away all background images and colorings on any button.
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-primary">Primary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-secondary">Secondary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-success">Success</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-info">Info</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-warning">Warning</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-danger">Danger</button>Extra content
Nevertheless the semantic button classes and outlined looks are truly outstanding it is necessary to keep in mind some of the page's targeted visitors will likely not truly have the capacity to observe them in such manner whenever you do have some a bit more special meaning you would love to add to your buttons-- ensure along with the aesthetic options you additionally provide a few words describing this to the screen readers hiding them from the page with the . sr-only class so really everybody could get the impression you desire.
Buttons sizing
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg">Large button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg">Large button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">Small button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-sm">Small button</button>Make block level buttons-- those that span the full width of a parent-- by adding .btn-block.
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg btn-block">Block level button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg btn-block">Block level button</button>Active mechanism
Buttons will appear pressed (with a darker background, darker border, and inset shadow) when active.
<a href="#" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg active" role="button" aria-pressed="true">Primary link</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg active" role="button" aria-pressed="true">Link</a>Disabled mode
Oblige buttons looking out of action through providing the disabled boolean attribute to any kind of <button> element.
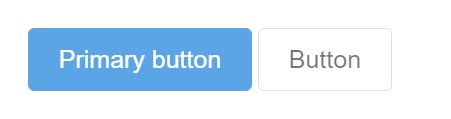
<button type="button" class="btn btn-lg btn-primary" disabled>Primary button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg" disabled>Button</button>Disabled buttons applying the <a> element work a bit different:
- <a>-s do not support the disabled attribute, in this degree you have to add the .disabled class to get it visually appear disabled.
- A few future-friendly styles are included to turn off each of the pointer-events on anchor buttons. In internet browsers which assist that property, you won't find the disabled arrow in any way.
- Disabled buttons have to provide the aria-disabled="true" attribute to signify the condition of the component to assistive technologies.
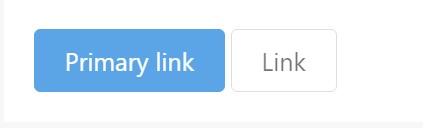
<a href="#" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg disabled" role="button" aria-disabled="true">Primary link</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg disabled" role="button" aria-disabled="true">Link</a>Link capabilities caveat
In addition, even in browsers that do support pointer-events: none, keyboard navigation remains unaffected, meaning that sighted keyboard users and users of assistive technologies will still be able to activate these links.
Toggle element
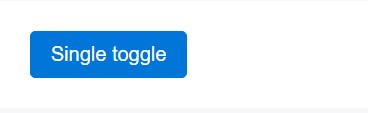
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="button" aria-pressed="false" autocomplete="off">
Single toggle
</button>A bit more buttons: checkbox plus radio
Bootstrap's .button styles can possibly be put on various other elements, including <label>- s, to provide checkbox or radio style button toggling. Add data-toggle=" buttons" to .btn-group containing those changed buttons to enable toggling in their various styles. The checked status for all of these buttons is only upgraded by using click event on the button. If you use some other method to update the input-- e.g., with <input type="reset"> or by manually applying the input's reviewed property-- you'll have to toggle .active on the <label> manually.
Take note of that pre-checked buttons require you to manually bring in the .active class to the input's <label>.
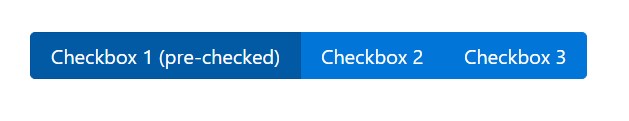
<div class="btn-group" data-toggle="buttons">
<label class="btn btn-primary active">
<input type="checkbox" checked autocomplete="off"> Checkbox 1 (pre-checked)
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Checkbox 2
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Checkbox 3
</label>
</div>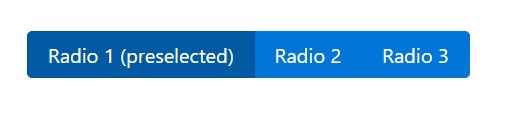
<div class="btn-group" data-toggle="buttons">
<label class="btn btn-primary active">
<input type="radio" name="options" id="option1" autocomplete="off" checked> Radio 1 (preselected)
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="radio" name="options" id="option2" autocomplete="off"> Radio 2
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="radio" name="options" id="option3" autocomplete="off"> Radio 3
</label>
</div>Options
$().button('toggle') - toggles push condition. Brings the button the visual appeal that it has been activated.
Final thoughts
Generally in the new version of the most popular mobile first framework the buttons evolved aiming to become more legible, more friendly and easy to use on smaller screen and much more powerful in expressive means with the brand new outlined appearance. Now all they need is to be placed in your next great page.
Check a couple of video clip training relating to Bootstrap buttons
Related topics:
Bootstrap buttons: official documentation
W3schools:Bootstrap buttons tutorial